Large language models for financial data analysis represent banking’s largest technology opportunity, and its most persistent disappointment. McKinsey estimates $200-340 billion in annual value.¹ Yet fewer than 5% of pilots reach production.²
The gap isn’t capability. Current models parse complex documents, extract entities, and synthesize insights across thousands of pages with remarkable fluency. The gap is precision. When leading models achieve roughly 80% accuracy on financial reasoning benchmarks³, the error rates can compound across thousands of documents. At that scale, human review consumes any efficiency gains.
Institutions that succeed share a common architecture: hybrid systems that combine LLM semantic capabilities with deterministic validation layers. JPMorgan’s COIN system saves 360,000 hours annually.⁴ Danske Bank’s fraud detection catches 60% more fraud with 50% fewer false positives.⁵ Neither achieved this through better models. They achieved it through better systems.
This guide provides the practitioner’s roadmap: model selection based on actual cost-performance trade-offs, validation architectures that bridge the accuracy gap, navigation of FINRA and EU AI Act requirements, and the 90-day implementation sequence that successful institutions follow. The path from pilot to production isn’t about finding smarter AI—it’s about building smarter systems around AI’s known limitations.
Key Takeaways
- The accuracy gap is solvable. LLMs achieve ~80% accuracy on financial benchmarks—insufficient alone, but hybrid architectures with deterministic validation reach 99%+.
- 95% of GenAI pilots fail due to flawed integration, not model limitations. Success requires narrow scope and preserved human oversight.
- Production winners share patterns. JPMorgan, Danske Bank, and Morgan Stanley all architected systems where AI handles semantic tasks while deterministic systems handle precision.
- Fine-tuning economics shifted. From-scratch training costs ~$2.7M; QLoRA delivers 99%+ performance for ~$100-300 on a single GPU.
- Regulatory timelines are concrete. EU AI Act: prohibitions (Feb 2025), governance (Aug 2025), full high-risk requirements (Aug 2026).
- Model selection hierarchy: data sensitivity → accuracy requirements → volume → latency. No model achieves 95%+ alone.
The Financial AI Reality Check
The numbers tell a paradox. AI venture capital exceeded $100 billion in 2024.⁶ Close to a third of all global venture funding went to AI companies in 2024, with nearly half in North America.⁷ 91% of financial services companies are either assessing AI or already using it in production.⁸
Then the success rates: fewer than 5% of generative AI pilots reach production deployment.²
This isn’t a story about overhyped technology. The capabilities are real. GPT and Claude demonstrate remarkable semantic understanding—parsing 10-K filings, extracting covenant terms from loan agreements, synthesizing earnings call transcripts into actionable summaries. The demonstrations work. The pilots succeed.
Production fails for a different reason: financial workflows demand accuracy levels that current models cannot guarantee alone. A roughly 80% accuracy rate sounds impressive in a research paper. In a compliance-sensitive environment processing thousands of documents daily, it means systematic error introduction at scale.
The institutions that crossed from pilot to production understood something crucial: the goal isn’t making LLMs more accurate. It’s making their accuracy verifiable.
How LLMs Transform Financial Data Analysis
The Implementation Success Pattern
Every successful large-scale financial AI deployment shares structural similarities—not in the models they chose, but in how they bounded the problem.
| Institution | What They Built | What They Achieved | What They Learned |
| JPMorgan | COIN contract analysis system | 360,000 hours saved annually⁴ | Start with document processing, not decision-making. |
| Danske Bank | Fraud detection with AI pattern recognition | 60% better detection, 50% fewer false positives⁵ | Combine models with rules-based validation. |
| Morgan Stanley | Wealth management research synthesis | 98%+ advisor adoption⁹ | Augment advisors, don’t replace judgment. |
The pattern: narrow scope, clear validation mechanisms, human oversight preserved where it matters. None of these institutions deployed general-purpose AI and hoped for the best. They architected systems where AI handles what AI does well—semantic understanding, pattern recognition, synthesis—while deterministic systems handle what they do well: precise calculation, rule application, compliance verification.
Failure Modes That Kill Financial AI Projects
LLM failures in financial applications aren’t random. They cluster into predictable categories, each requiring different architectural responses.
Numerical Hallucinations
An LLM correctly identifies that revenue appears on page 47 of a 10-K filing. It extracts “$4.2 billion.” The actual figure is $4.8 billion. The model didn’t misread—it confabulated. This happens with disturbing regularity, even when source documents are unambiguous.
The solution isn’t better prompting. It’s architectural: never let LLMs perform numerical extraction without deterministic verification against source documents. The model proposes; validated data confirms.
Semantic Drift
A typical 10-K filing runs tens of thousands of words. Over extended context, LLMs lose coherence. Early context degrades. Cross-references break. A question about Q3 performance retrieves Q1 data because the embeddings look similar enough.
The solution: element-based chunking that preserves semantic boundaries. Tables stay intact. Footnotes remain linked to their referents. Fiscal periods carry explicit metadata. Studies suggest this approach meaningfully improves retrieval accuracy compared to naive token-based chunking—a gap that compounds across thousands of queries.
Confident Fabrication
The most dangerous failure mode: presenting false information with high confidence. An LLM asserts that a company’s debt-to-equity ratio improved year-over-year when it actually deteriorated. No hedging language. No uncertainty markers. Just wrong, confidently.
Multi-layer mitigation is required: NLI validation comparing outputs against source documents, confidence scoring with calibrated thresholds, multi-model consensus for material claims. When two different model architectures agree on a fact that matches source verification, reliability increases substantially.
Building Production-Ready Financial LLM Systems
The Three-Layer Architecture
Production financial document processing follows a consistent structure across successful implementations.
Layer 1: Ingestion
The unglamorous foundation that determines everything downstream. EdgarTools provides structured XBRL access to SEC filings, eliminating much of the PDF-to-structured-data pipeline that often consumes significant implementation effort. Unstructured.io handles element detection—identifying tables, headers, and paragraphs as distinct semantic units rather than continuous text streams.
The key insight: how you chunk documents determines retrieval quality. Element-based chunking preserves structure. A financial table with footnote references stays linked. A multi-paragraph discussion of risk factors remains coherent. Token-based chunking that splits mid-sentence destroys context for everything downstream.
Layer 2: LLM Processing
Semantic understanding happens here—entity extraction, classification, summarization, relationship identification. The critical discipline: constrain what you ask the LLM to do.
Effective prompt architecture separates reasoning from calculation:
financial_analysis_prompt = “””
Role: Senior financial analyst reviewing document.
CONSTRAINTS:
– IDENTIFY calculations needed but DO NOT perform them
– CITE line items by exact name and value from source
– FLAG patterns requiring human review
Document: {document_text}
Output:
1. Metrics Identified: [List without calculating]
2. Required Formulas: [Methodology only]
3. Source Values: [Exact figures from document]
4. Risk Flags: [Anomalies detected]
“””
This separation—LLM identifies what needs calculating, deterministic systems perform calculations—can meaningfully improve accuracy on complex financial reasoning tasks.
Layer 3: Validation
Every numerical claim follows dual paths: LLM extraction and source document verification. Discrepancies trigger escalation. Confidence scores below defined thresholds route to human review. Audit trails capture everything for regulatory defensibility.
This layer transforms an AI experiment into a production system.
Why Standard RAG Fails on Financial Documents
Retrieval-Augmented Generation promises to ground LLM outputs in source documents. In practice, vanilla RAG fails catastrophically on financial content.
The reason: financial documents contain dense, interconnected numerical relationships that produce near-identical embeddings for semantically distinct content. “Q3 2024 revenue was $4.2B” and “Q3 2023 revenue was $4.2B” occupy nearly the same point in vector space. A query about current revenue might retrieve last year’s figure. The model would never know the difference.
Production-grade RAG for financial applications requires hybrid retrieval—combining vector similarity for semantic matching with keyword matching for exact terms like tickers, dates, and specific amounts. Add temporal metadata filtering so queries respect fiscal periods. Implement entity linking so “Apple’s latest 10-K” resolves to the correct document, section, and table. Preserve hierarchical relationships between tables and their footnotes.
This architecture achieves significant reduction in retrieval failures compared to standard implementations—the difference between a system that mostly works and one reliable enough for production.
Fine-Tuning Economics
For most production use cases, fine-tuning existing models delivers the vast majority of value at a fraction of the cost. Reserve from-scratch training for institutions with unique proprietary data advantages and multi-year investment horizons.
Effective fine-tuning datasets for financial applications include DISC-Fin-SFT (250,000 financial instruction examples), FinQA (numerical reasoning focus), and Financial PhraseBank (sentiment baseline).
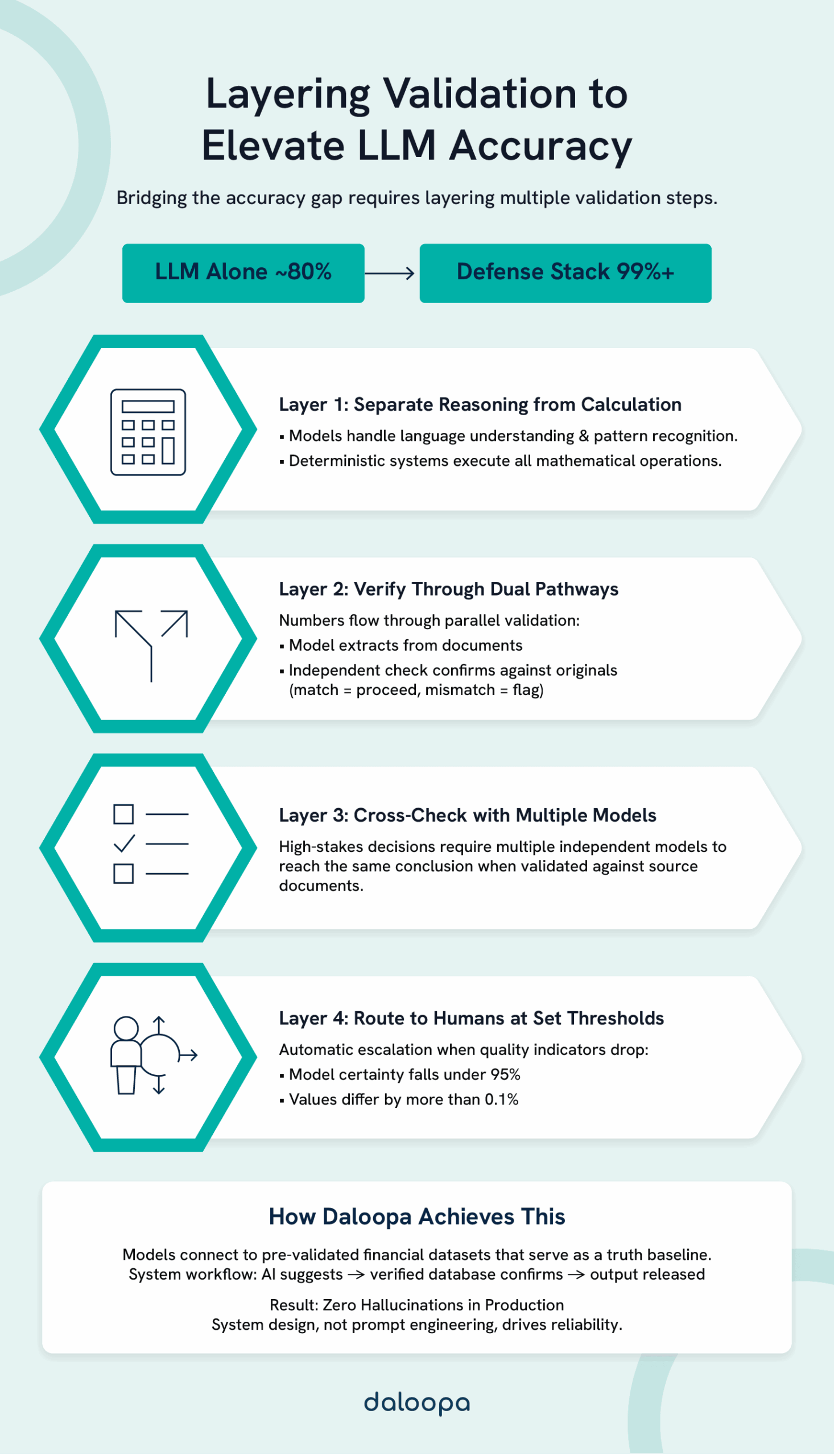
Solving the Accuracy Problem
From 80% to 99%: The Layered Defense
Bridging the accuracy gap requires layering multiple validation mechanisms.
Layer 1: Architectural Separation — Never trust LLM math. Use models for semantic tasks; route all numerical operations through deterministic systems.
Layer 2: Dual-Path Validation — Every numerical claim travels two paths: LLM extraction and source verification. Agreement proceeds; discrepancy triggers review.
Layer 3: Multi-Model Consensus — For material decisions, require agreement across different model architectures checking against verified source data.
Layer 4: Calibrated Human Escalation — Define explicit thresholds. Confidence below 95% escalates. Numerical discrepancies above 0.1% escalate. The goal is focusing human attention where it matters most.
The Daloopa Approach
Daloopa’s architecture demonstrates these principles in production: LLMs connect to verified datasets as ground truth. The model proposes extractions; the verified data layer validates them. This achieves what prompt engineering alone cannot—LLM financial accuracy that’s verifiable rather than aspirational. The 0% hallucination rate isn’t magic; it’s architecture.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory frameworks are converging globally. Practitioners need specific timelines and concrete requirements for AI regulatory compliance in finance.
United States: FINRA and SEC
FINRA Notice 24-09 (July 2024) established the current framework for AI in securities. Technology governance must explicitly address AI-specific risks. Prior approval workflows are required for AI-generated client communications. Supervision systems must monitor for model drift and performance degradation over time. Model risk management programs under SR 11-7 apply to AI systems used in covered activities.
The SEC has signaled increasing focus on AI disclosure requirements and is actively examining how firms represent AI capabilities to clients.
European Union: AI Act Timeline
The EU AI Act creates binding obligations on a defined schedule:¹⁰
- August 2024: Act entered into force
- February 2025: Prohibitions on unacceptable-risk AI applications took effect
- August 2025: Governance rules and general-purpose AI model requirements applied
- August 2026: Full application for high-risk AI systems, including most financial services applications
Non-compliance penalties reach €35 million or 7% of global annual revenue—whichever is higher.
Practical Compliance Posture
- Document AI governance frameworks with board-level approval.
- Extend model risk management programs to cover AI-specific failure modes.
- Implement human approval workflows for client-facing AI outputs.
- Maintain audit trails capturing model versions, inputs, outputs, and validation results.
- Conduct and document bias testing before deployment.
- Define human oversight protocols for automated decisions.
Consult your compliance team for guidance on specific implementations. Regulatory interpretation continues evolving.
Preventing and Detecting Hallucinations
Hallucination risk requires defense in depth:
- Prevention through domain-specific training data, RAG grounded in verified sources, and prompt constraints.
- Detection via NLI validation, calibrated confidence scoring, and anomaly detection.
- Mitigation with human review for material claims and fallback to rules-based systems.
- Recovery through clear escalation paths, model versioning, and incident documentation.
The goal isn’t eliminating hallucinations—current technology can’t guarantee that. The goal is catching them before they cause harm.
Use Cases with Realistic ROI
Financial Statement Analysis
Production performance expectations with proper validation architecture:
| Metric | Reality |
| Text extraction accuracy | 95%+ achievable |
| Numerical accuracy | 99%+ with deterministic verification |
| Processing time reduction | 33-50% |
| Cost savings | ~40% reduction in analysis labor |
| Implementation timeline | 4-6 months for production-ready system |
The implementation sequence that works: start with document summarization (low risk, high learning value), add data extraction with validation layers, implement ratio calculations with deterministic verification, then scale toward fuller automation while preserving human oversight for material judgments.
Earnings Call Analysis
Sentiment analysis accuracy varies dramatically by method:
| Approach | Accuracy | Trade-off |
| Traditional NLP | 40-45% | Low cost, limited nuance |
| FinBERT fine-tuned | ~52% | Moderate cost, financial domain awareness |
| GPT with proper prompting | 74-81% | Higher cost, superior context handling |
One important caveat: stock price prediction from sentiment analysis remains unreliable—studies show 40-61% accuracy, barely better than chance. Use sentiment analysis for qualitative insight generation, not trading signals.
Fraud Detection
Fraud detection represents one of the stronger ROI cases in financial AI:
| Outcome | Improvement |
| Detection rate | 50-300% better catch rates |
| False positive reduction | 60-80% fewer false alarms |
| Processing capacity | 1.8M+ transactions/hour |
| ROI timeline | 6-12 months typical |
The false positive reduction often drives ROI more than detection improvement. Every false positive requires human investigation. Legacy systems generate massive investigation backlogs. Reducing false positives by 60-80% while improving actual detection fundamentally changes unit economics.
Choosing the Right Model
Decision Framework
Model selection follows a decision hierarchy.
First: Data Sensitivity — High sensitivity requirements mandate self-hosted deployment. No API calls leaving your infrastructure. This constrains options significantly but isn’t negotiable for certain use cases.
Second: Accuracy Requirements — Above 95% accuracy requirements mandate hybrid architecture with validation layers. No model achieves this alone on complex financial reasoning.
Third: Volume — Above 100 million tokens monthly, cost optimization becomes critical. The difference between $0.40 and $60 per million tokens compounds quickly.
Fourth: Latency — Real-time requirements (sub-300ms) limit model choices. Most production financial workflows tolerate 1-3 second response times.
Recommended Architecture
A three-tier approach balances capability, cost, and risk:
| Tier | Volume Share | Model Class | Application |
| Tier 1 | ~10% | Self-hosted (Llama) | Sensitive analysis requiring data sovereignty |
| Tier 2 | ~70% | API-based (Claude, GPT) | Production workloads with standard sensitivity |
| Tier 3 | ~20% | High-speed (Gemini Flash) | Classification, routing, high-volume preprocessing |
A note on open source: Self-hosted models aren’t free. Production-grade deployment of a 70B parameter model requires $15-25K monthly in infrastructure—GPU instances, monitoring, redundancy, maintenance. Factor this into total cost of ownership calculations.
Future-Proofing Your Implementation
What’s Available Now
Multimodal Analysis: Current models process charts, tables, and text in unified context.
Agentic Workflows: Models execute multi-step research tasks with minimal human intervention per step.
Knowledge Graph Integration: Connecting LLMs to structured knowledge graphs enables explainable reasoning chains.
Build systems now with audit trails, model versioning, and documentation practices that anticipate increasing regulatory scrutiny.
The 90-Day Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1-4)
Investment: Under $1,000/month
Deliverables:
- Use case inventory with prioritization matrix
- Risk assessment using NIST AI Risk Management Framework
- Gap analysis of current technology capabilities
- Implementation roadmap with resource requirements and budget
Success criteria: Clear scope definition, stakeholder alignment, realistic timeline established
Phase 2: Pilot (Months 2-4)
Investment: $1,000-5,000/month
Deliverables:
- Low-risk application deployed (document summarization recommended)
- Basic infrastructure operational
- Initial validation framework tested
- Performance baseline established
Success criteria: Accuracy meets or exceeds baseline, zero security incidents, user feedback positive
Phase 3: Production (Months 5-8)
Investment: $5,000-20,000/month
Deliverables:
- Full architecture deployed with validation layers
- Monitoring and alerting operational
- Governance framework documented
- Compliance documentation complete
Success criteria: Positive ROI trajectory, regulatory approval obtained, error rates within tolerance
Phase 4: Scale (Months 9-12+)
Investment: Variable based on volume
Deliverables:
- Expanded use case coverage
- Advanced capabilities deployed
- Optimization program operational
- Continuous improvement metrics tracked
Success criteria: 40%+ cost reduction versus manual processes, sub-1% error rates sustained
Your Action Plan
Three workstreams, running in parallel:
Technical Track
- Weeks 1-2: Install EdgarTools and Unstructured.io; test on sample documents
- Weeks 3-4: Deploy vector database with hybrid retrieval configuration
- Weeks 5-8: Build pilot RAG system with validation layer
- Weeks 9-12: Production hardening—monitoring, alerting, failover
Organizational Track
- Weeks 1-2: Form AI steering committee with executive sponsorship
- Weeks 3-4: Conduct risk assessment; prioritize use cases by value and feasibility
- Weeks 5-8: Develop governance framework; define escalation protocols
- Weeks 9-12: Train operations staff on prompt engineering and oversight responsibilities
Compliance Track
- Weeks 1-2: Review FINRA 24-09 requirements against planned implementation
- Weeks 3-4: Assess EU AI Act applicability and timeline
- Weeks 5-8: Implement audit trail systems; document model governance
- Weeks 9-12: Conduct first internal compliance review; remediate gaps
The Path Forward
The path from pilot to production isn’t about finding a better model—every major LLM performs within a similar accuracy band. Success comes from architecting systems that make AI accuracy verifiable: semantic capabilities paired with deterministic validation, human judgment preserved where it matters, audit trails that satisfy regulators.
Daloopa’s LLM integration demonstrates this architecture in production: verified datasets as ground truth, validation layers that catch errors before they propagate, 0% hallucination rates through system design rather than prompting alone.
The opportunity remains enormous. The implementation path is now clear. The question isn’t whether LLMs will transform financial analysis—it’s whether your institution will be among the 5% that successfully make the transition.
See how Daloopa accelerates your implementation →
References
- “Scaling Gen AI in Banking: Choosing the Best Operating Model.” McKinsey & Company, 22 Mar. 2024.
- “MIT report: 95% of generative AI pilots at companies are failing.” Fortune, 18 Aug. 2025.
- “Benchmark of 30 Finance LLMs: GPT-5, Gemini 2.5 Pro & More.” AIMultiple Research, 25 Nov. 2025.
- “An AI Completed 360,000 Hours of Finance Work in Just Seconds.” Futurism, 8 Mar. 2017.
- “Danske Bank and Teradata Implement Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engine that Monitors Fraud in Real Time.” PR Newswire/Teradata, 23 Oct. 2017.
- “Startup Funding Regained Its Footing In 2024 As AI Became The Star Of The Show.” Crunchbase News, 7 Jan. 2025.
- “AI Startups Grabbed a Third of Global VC Dollars in 2024.” PitchBook, 10 Jan. 2025.
- “AI Takes Center Stage: Survey Reveals Financial Industry’s Top Trends for 2024.” NVIDIA Blog, 11 Jan. 2024.
- “Morgan Stanley Wealth Advisors Are About to Get an OpenAI-Powered Assistant.” CNBC, 26 Jun. 2024.
- “Implementation Timeline.” EU Artificial Intelligence Act, 2025.



